Once the concrete has been mixed it needs to be placed and compacted. These two activities are carried out simultaneously. Placing and compaction of concrete should be done without causing any segregation of its ingredients. When placing the concrete, care need to be taken not to damage the form work or dislodge the reinforcement. The following process takes place:
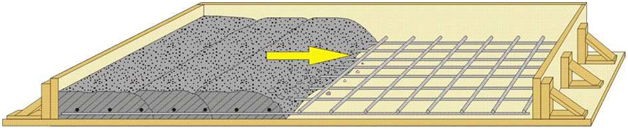
- Placing the concrete starts from the corners of the form work with compaction of the concrete starting immediately after it has been placed. The concrete should be placed in layers not higher than 30 cm when compacted by hand and in layers not higher than 60 cm when compacted by vibration.
- Slabs and floors should be poured in one continuous operation to avoid any vertical or horizontal joints, which can create planes of weaknesses within the structure.
- If the concrete is not properly compacted, air will remain inside the pour. When it hardens, the concrete then appears with honeycomb spots or rashes. As these spots contain a considerable amount of air, they compromise the strength and impermeability of the concrete.
- Consolidation/compaction can be done by hand with hand-tampers or iron rods.
- A more effective method is to use a poker vibrator. The vibrator is immersed into the concrete at regular intervals of half a metre apart. Vibration should not be longer than 10 seconds in one place and the vibrator should be kept away from the form work and reinforcement bars. Excessive vibration causes the aggregate to segregate.
- If concrete is not properly poured and compacted, honeycombing and voids will be formed which weakens the structure.
- After the concrete has been properly compacted, the top of the concrete is levelled to a smooth surface with a mason’s trowel or a float. For large surfaces, a straight edge is used as a screed for levelling the concrete. The straight edge is worked back and forth in a sawing fashion to level the entire surface of the concrete.
- Make sure that the correct volume of concrete is poured to the levels marked inside the form works. Keep an eye on the reinforcement and ensure that the concrete adequately covers the reinforcement bars.
Proper curing essentially consists of keeping the concrete moist during the period during which it is gaining strength. This is secured either by containing the water already added to the concrete when it was poured or by replenishing its surfaces with additional water to compensate for any water lost through evaporation. The most common method of keeping concrete moist is by frequently sprinkling or flooding the surface, or by covering the surface with wet gunny bags. Covering the surfaces with plastic sheets, banana or palm leaves or other materials also reduces the evaporation from bright sun and wind. Delaying the removal of the form works as long as possible also reduces moisture loss.
