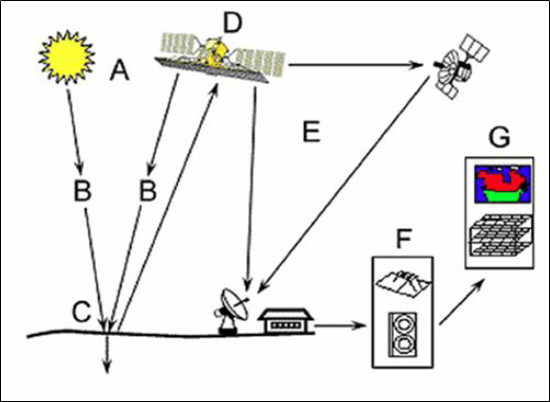
Remote sensing is a revolutionary change in surveying in which objects on the earth are sensed from remote places like aircraft or satellites and are used in map making. It always goes with Geographical Information System (GIS) which is a software tool used for the analysis of remotely sensed data with the help of the computers.
It may be defined as art and science of collecting information about objects, area or phenomenon without having physical contact with it. Eye sight and photographs are common examples of remote sensing in which sunlight or artificial light energy from electricity is made to strike the object. Light energy consists of electromagnetic waves of all length and intensity. When electromagnetic wave falls on the object, it is partly
- absorbed 2. scattered 3. transmitted 4. reflected.
Different objects have different properties of absorbing, scattering, transmitting and reflecting the energy. By capturing reflected waves with sensors, it is possible to identify the objects. However, this remote sensing has its own limitations in terms of distance and coverage of area at a time. Photographic survey, in which photographs taken from aircrafts are used for map making, fall under this category of remote sensing. Using electronic equipment’s, this basic remote sensing technique is extended to identifying and quantifying various objects on the earth by observing them from longer distances from the space.
For this purpose, geostationary satellites are launched in the space, which rotate around the earth at the same speed as earth. Hence the relative velocity is zero and they appear stationary when observed from any point on the earth. Depending upon the property of the object, the electromagnetic waves sent from the satellite reflected energy is different. The reflected waves in the bandwidth of infrared, thermal infrared and micro waves are picked up by sensors mounted on satellite.
Since each feature on the earth has different reflection property, it is possible to identify the features on the earth with satellite pictures. Data obtained from satellites are transferred to ground stations through RADARS where user analyses to find out the type of object and the extent of it. This is called image processing. For quantifying the objects computers are used. India is having its own remote sensing satellites like IRS-series, INSAT series and PSLV series.
Application of Remote Sensing
Various applications of remote sensing may be grouped into the following:
- Resource exploration 2. Environmental study 3. Land use 4. Site investigation 5. Archaeological investigation and 6. Natural hazards study.
- Resource Exploration:Geologists use remote sensing to study the formation of sedimentary rocks and identify deposits of various minerals, detect oil fields and identify underground storage of water. Remote sensing is used for identifying potential fishing zone, coral reef mapping and to find other wealth from ocean.
- Environmental Study: Remote sensing is used to study cloud motion and predict rains. With satellite data it is possible to study water discharge from various industries to find out dispersion and harmful effects, if any, on living animals. Oil spillage and oil slicks can be studied using remote sensing.
- Land Use:By remote sensing, mapping of larger areas is possible in short time. Forest area, agricultural area, residential and industrial area can be measured regularly and monitored. It is possible to find out areas of different crops.
- Site Investigation:Remote sensing is used extensively in site investigations for dams, bridges, pipelines. It can be used to locate construction materials like sand and gravel for the new projects.
- Archaeological Investigation:Many structures of old era are now buried under the ground and are not known. But by studying changes in moisture content and other characteristics of the buried objects and upper new layer, remote sensors are able to recognize the buried structures of archaeological importance.
- Natural Hazard Study:Using remote sensing the following natural hazards can be predicted to some extent and hazards minimized:
- Earthquake 2. Volcanoes 3. Landslides 4. Floods and 5. Hurricane and cyclones.
GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS)
Maps are used as the languages of simple geography. Importance of map making is recognized long ago. Surveyors went round the land and prepared maps. Data required for locating and calculating extent of a place/region is called spatial data.
Physical properties and human activities related to a place/region are stored in the form of tables, charts and texts. This information is called attribute data. Referring to maps/plans and then to attribute data stored in hard copies like books is time consuming updating and managing the data is difficult. This problem is overcome by combining spatial data and attribute data of the location by appropriate data base management in computers.
The location information (spatial data) is digitised from available maps and stored in computers. For this data structure used is either raster data or vector data format. In raster data structures pick cells are associated with the spatial information, while in vector data structure coordinates are associated with each region and sub-regions. Over the spatial data attribute data is overlayed and stored. Once this geographical information system is developed, the user can access the attribute data of any place by clicking over the spatial data of that place.
The user can utilise the information for further analysis, planning or for the management. For example, if land records of a village is developed as GIS data, the user can click the state map to pick up the district map and then access taluka map. Then he will access it to pick up the village map. Then land record of that village can be obtained and property map of any owner can be checked and printed. All this can be achieved in a very short time from any convenient place. Remote sensing and GIS go hand in hand, since lot of data for GIS is from remote sensing. Remote sensing needs GIS for data analysis. Some of the areas of GIS application are:
- drainage systems 2. streams and river basins management 3. lakes 4. canals 5. roads 6. railways 7. land records 8. layout of residential areas 9. location of market, industrial, cultural and other utilities 10. land use of different crops etc.
The above information helps in planning infrastructural development activities such as planning roads, rail routes, dams, canals, tunnels, etc. It helps in taking steps to check hazards of soil erosion and the challenges in future.